Solar panels are a type of technology that converts sunlight into electricity. They work by using photovoltaic cells, which are made up of layers of silicon and other materials.
When sunlight hits these cells, it causes electrons to move, creating an electric current. This is known as the photovoltaic effect. The electricity generated by solar panels can be used to power homes, businesses, and even vehicles.
Solar power is becoming increasingly popular as a renewable energy source due to its environmental benefits and decreasing costs. We will explain how do solar panels work, what they are made of, and the materials used to make them.
We’ll also delve deeper into the photovoltaic effect and its importance for panel efficiency. Additionally, we’ll discuss how solar panels convert photons to electricity and the role of inverters in converting DC to AC power.

Contents
- 1 Discussion On How Do Solar Panels Work
- 1.1 Understanding The Photovoltaic Effect
- 1.2 Different Types Of Solar Panel Materials
- 1.3 Importance Of Solar Panel Efficiency
- 1.4 How Do Solar Panels Convert Photons To Electricity?
- 1.5 The Role Of Inverters In Converting DC To AC
- 1.6 Powering Home Appliances With Solar Electricity
- 1.7 How Many Modules Are Needed To Power A Home?
- 1.8 How Does Solar Power Work During Winter?
- 1.9 Monocrystalline Vs. Polycrystalline Modules
- 1.10 Financing Options For Going Solar
What Are Solar Panels Made Of?
Solar panels comprise several layers of materials that work together to produce electricity from sunlight. The most important material in solar panels is silicon, a semiconductor that can convert sunlight into electrical energy.
The silicon layer between two sheets of conductive material, usually metal, and encased in a protective glass or plastic layer. When sunlight hits the solar panel, it excites the electrons in the silicon, causing them to move and create an electric current. This electricity can then use to power homes and businesses.
Some solar panels also include additional layers of materials, such as anti-reflective coatings or back sheets, to improve their efficiency and durability. These various materials allow solar panels to harness the sun’s power and convert it into usable energy for our daily needs.
Discussion On How Do Solar Panels Work

Solar panels are a renewable energy source that converts sunlight into usable electricity through the use of photovoltaic cells. These cells are made up of layers of silicon, which absorbs photons from the sun’s rays and converts them into electrons. These electrons are then collected by an electrical circuit and directed to a battery or power grid for storage or immediate use.
The process of converting sunlight into electricity is complex, but it all starts with the solar panel itself. When sunlight hits the panel, it excites the electrons in the silicon atoms, causing them to move around and generate an electric current. This current can then be used to power homes, businesses, and other devices.
While solar panels have been around for decades, recent advancements in technology have made them more efficient and affordable than ever before. As a result, more and more people are turning to solar energy as a way to reduce their carbon footprint and save money on their energy bills.
Whether you’re interested in installing solar panels on your home or simply curious about how they work, understanding the science behind this incredible technology is sure to impress.
Understanding The Photovoltaic Effect
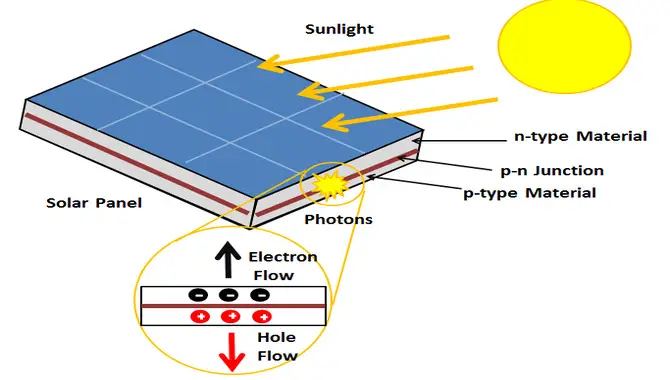
The process that explains how do solar panels work is called the photovoltaic effect. When photons from the sun’s rays hit a solar cell made of semiconductor materials such as silicon or thin-film materials like CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide), they knock electrons loose from atoms within the cell.
As a result, an electric current can convert into AC electricity by an inverter for home appliances or fed back into the grid. However, direct current (DC) energy produced by a solar panel must go through an inverter before it enters the electrical panel and powers your home appliances.
Different Types Of Solar Panel Materials
Solar panel technology has come a long way since its inception. Today, various types of solar panel materials are available to customers who want to switch to clean energy. Among them are polycrystalline, monocrystalline, thin-film, and bifacial solar panels.
While polycrystalline solar panels are less expensive than other types, they have lower efficiency rates due to their multiple silicon crystal structure. Monocrystalline solar panels have higher efficiency rates than polycrystalline ones; however, they come at a higher price point because they’re made of a single silicon crystal.
Thin-film solar panels are lightweight and flexible but less efficient than crystalline ones. Lastly, bifacial solar panels capture sunlight reflected off the ground or surrounding surfaces from both sides, making them incredibly effective.
Importance Of Solar Panel Efficiency

The efficiency of a solar panel system depends on many factors, such as temperature, shading, and orientation. Solar panels need regular maintenance and cleaning to operate at their best. Choosing the right panel type for your needs maximizes efficiency and savings. Although high-efficiency solar panels may be more expensive upfront, they can save you money in the long term.
Inverters play a key role in converting DC electricity produced by solar cells into AC electricity that powers home appliances. By using renewable energy from the sun’s rays, homeowners can reduce their reliance on the grid and contribute to a cleaner energy future.
How Do Solar Panels Convert Photons To Electricity?

Solar panels work by converting photons, or light particles, into electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. This process occurs within the solar cells that make up the solar panel. Each cell comprises two layers of silicon, one with extra electrons and one with missing electrons.
When photons from the sun hit the solar cell, they knock loose some of the electrons in the top layer, which creates an electric current that flows through a circuit in the panel. This current can then use to power appliances or stored in batteries for later use.
The efficiency of a solar panel depends on factors such as the amount of sunlight it receives and its temperature. However, with advances in technology and increased accessibility, solar energy is becoming more affordable and widely used as a renewable source of electricity.
The Role Of Inverters In Converting DC To AC
Solar panel systems produce DC electricity. For it to use in home appliances or businesses, DC must convert to AC electricity with the help of an inverter. Solar panels use photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into an electrical current that flows through wires to the inverter.
There are different types of inverters which can use for this process. They include string inverters, microinverters and power optimizers. Choosing the right one will ensure maximum energy production from your solar array.
Powering Home Appliances With Solar Electricity
Remember a few things if you’re considering powering your home appliances with solar power. Solar panels convert the sun’s energy into DC electricity through photovoltaic cells made of semiconductor material like silicon. The electrons knocked loose from atoms create an electric field that produces electrical current flow.
An inverter converts this DC electricity to AC, which can be used directly or stored using solar batteries for later use. Switching to renewable energy like solar power can reduce your carbon footprint and save you money on electricity bills.
How Many Modules Are Needed To Power A Home?

The ideal number of solar panels to power a home varies depending on energy consumption, location, and climate. Generally, a US home may require 20-30 solar panels. The size and quality of the panels impact their efficiency. Consult an expert to determine the best type and number of solar panels needed for your home. Solar panels convert sunlight into DC electricity, which an inverter converts into AC electricity.
How Does Solar Power Work During Winter?

Solar panels work by converting sunlight into electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. But what happens during winter when the days are shorter, and there is less sunlight? While solar panels produce less energy during the winter months, they can still generate power as long as they receive some sun.
Colder temperatures can improve solar panel efficiency by reducing resistance in electrical circuits. Additionally, snow on the panels can reflect light and increase their output. However, keeping the discussions clear of snow and debris is important to maximize their efficiency.
Overall, while solar panel output may be lower during the winter, they can still provide a valuable renewable energy source for your home or business.
Monocrystalline Vs. Polycrystalline Modules
Solar panel technology has advanced over the years, with monocrystalline and polycrystalline modules being two popular choices for homeowners looking to install a solar energy system. Monocrystalline panels have pure silicon cells, making them highly efficient in converting the sun’s energy into electrical current.
On the other hand, polycrystalline panels use a semiconductor material made by melting many fragments of silicon together, making them less expensive but less efficient. Both types generate direct current (DC) electricity that converts to alternating (AC) electricity using an inverter.
Homeowners can use excess energy generated by their solar panel system to offset their utility bills through net metering or store it in solar batteries for use during cloudy days.
Financing Options For Going Solar

You don’t have to make an upfront payment while going solar with financing options like solar leases, power purchase agreements (PPAs), and loans available. With a solar lease, you can lease the panels for a set period and pay affordable monthly fees.
PPAs let you buy electricity generated by the discussions at fixed rates. Loans help finance panel costs over time. Before choosing financing options suitable for your needs, research all available options.
Conclusion
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through a process known as the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the solar panel cells, it causes electrons to be released and flow through the cells, creating an electric current. Homes and businesses can power by this current.
While the technology behind solar panels may seem complex, their benefits are clear: they provide renewable energy that is clean, sustainable, and cost-effective in the long run. As we continue to seek ways to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and protect our planet’s resources, solar power remains a promising solution for a greener future.
Solar panels offer a sustainable and renewable energy source that can help reduce your carbon footprint and save you money on utility bills. Understanding how do solar panels work is crucial to make informed decisions about the type of solar panel system that suits your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.What Are The Benefits Of Using Solar Panels?
Ans: Using solar panels has many benefits, including reducing reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels, lower electricity bills over time, a smaller carbon footprint to combat climate change, and the possibility of tax incentives or rebates depending on location.
2.Can I Use A Solar Panel In My House?
Ans: Solar panels in your home are possible as they convert sunlight into electricity and reduce energy bills while benefiting the environment. It’s essential to consult a professional to determine if it’s a suitable option for your home.
3.Which Type Of Solar Panels Should I Buy For My Home?
Ans: Choosing the best solar panels for your home depends on your budget and energy needs. Monocrystalline panels offer high efficiency but come at a higher cost, while polycrystalline panels are less expensive but less efficient. Thin-film solar panels are the least costly but also the least efficient. It’s best to consult a trusted solar panel installer to make an informed decision.
4.What Is The Basic Science Behind Solar Panels?
Ans: Solar panels use photovoltaic cells made of silicon to convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the cells, it creates an electric field that generates electricity by pushing electrons to flow in a circuit. The electricity produced depends on sunlight intensity, duration, and efficiency of panel technology.
5.How Do Solar Panels Convert Sunlight Into Electricity?
Ans: Solar panels use photovoltaic cells made of silicone and other materials to create an electric field. When sunlight hits the cells, electrons are released, creating a flow of electricity. This can be used immediately or stored in batteries for later use.
Leave a Reply